Nicotine, a chemical compound found in tobacco plants, is a highly addictive substance that has profound effects on the human brain. With the rise of alternative nicotine delivery systems such as vaping and nicotine pouches, understanding how nicotine affects the brain has become increasingly important. This article will delve into the mechanisms of nicotine’s action on the brain, its short-term and long-term effects, and the specific impacts of vaping and nicotine pouches.
Mechanisms of Nicotine Action on the Brain
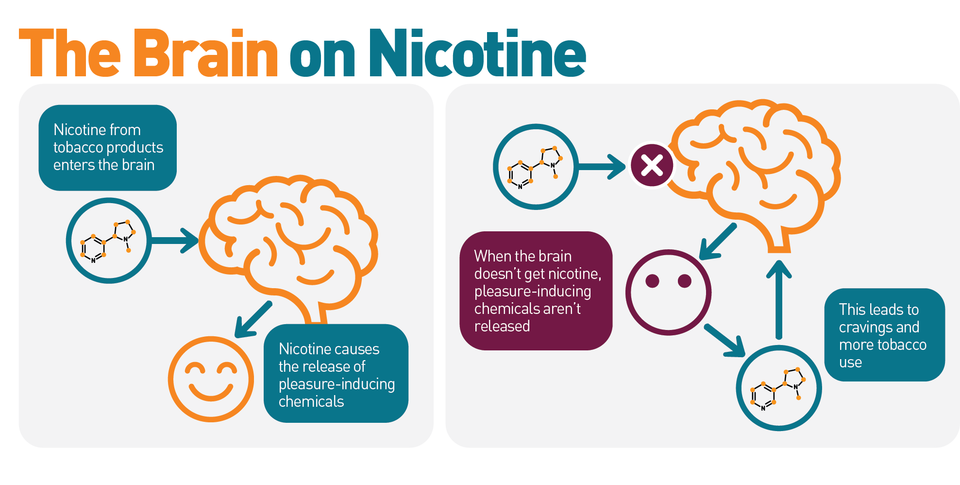
Nicotine exerts its effects primarily by interacting with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in the brain. These receptors are part of the cholinergic system, which plays a crucial role in cognitive functions, mood regulation, and reward processing.
- Binding to nAChRs: When nicotine enters the brain, it binds to nAChRs, leading to the release of several neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin.
- Dopamine Release: The stimulation of nAChRs in the brain’s reward pathways, particularly the mesolimbic pathway, results in the release of dopamine. This surge in dopamine creates feelings of pleasure and reward, contributing to nicotine’s addictive properties.
Short-Term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain
- Increased Alertness and Concentration: Nicotine can enhance cognitive functions such as attention, learning, and memory by modulating the release of acetylcholine and other neurotransmitters.
- Mood Regulation: Nicotine can improve mood and reduce anxiety in the short term due to its effects on dopamine and serotonin release. This is why some individuals use nicotine as a coping mechanism for stress.
- Addiction and Dependence: The pleasurable sensations and mood regulation effects of nicotine lead to the development of addiction. The brain quickly adapts to the presence of nicotine, resulting in tolerance and dependence.
Long-Term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain
- Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Decline: Chronic nicotine exposure can alter brain structure and function. Studies have shown that long-term nicotine use can affect neuroplasticity, potentially leading to cognitive decline and impairments in memory and learning.
- Mental Health Disorders: Prolonged nicotine use is associated with an increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. This is partly due to the changes in neurotransmitter systems caused by chronic nicotine exposure.
- Addiction Cycle: Long-term nicotine use leads to a vicious cycle of addiction. The brain’s reward system becomes dependent on nicotine to release dopamine, making it difficult for individuals to quit.
Effects of Vaping on the Brain
Vaping, the act of inhaling vapor produced by an electronic cigarette or similar device, delivers nicotine without the harmful byproducts of combustion found in traditional cigarettes. However, the impact of vaping on the brain is still significant.
- Nicotine Delivery: Vaping devices are designed to deliver nicotine efficiently, often resulting in higher nicotine intake compared to traditional smoking. This can enhance the addictive potential and exacerbate the effects on the brain’s reward system.
- Adolescent Brain Development: The adolescent brain is particularly vulnerable to the effects of nicotine. Vaping among teenagers can lead to alterations in brain development, affecting areas involved in decision-making, impulse control, and emotional regulation.
- Neuroinflammation: Emerging research suggests that the chemicals in e-liquids, aside from nicotine, can cause inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, potentially leading to neurodegenerative diseases.
Effects of Nicotine Pouches on the Brain
Nicotine pouches are another alternative nicotine delivery system that provides a smokeless and often discreet way to consume nicotine. They contain nicotine and other ingredients, but no tobacco.
- Controlled Nicotine Release: Nicotine pouches provide a slower and more controlled release of nicotine compared to smoking and vaping. This can potentially reduce the intensity of nicotine’s immediate effects on the brain.
- Reduced Exposure to Harmful Substances: While nicotine pouches eliminate the harmful byproducts of combustion, the effects of nicotine alone on the brain remain significant. The addictive potential and impact on cognitive functions are similar to other nicotine delivery systems.
- Behavioral and Psychological Effects: Regular use of nicotine pouches can lead to similar addictive behaviors and psychological effects as other forms of nicotine consumption, including dependence, mood alterations, and cognitive impairments.
Conclusion
Nicotine has profound and multifaceted effects on the brain, influencing neurotransmitter release, cognitive functions, mood, and addiction pathways. While alternative nicotine delivery systems like vaping and nicotine pouches may reduce some of the health risks associated with traditional smoking, they still pose significant risks to brain health. Understanding the mechanisms and effects of nicotine on the brain is crucial for developing effective public health strategies and helping individuals make informed decisions about nicotine use.
For more detailed information and authoritative data on nicotine and its effects on the brain, refer to sources such as the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and peer-reviewed studies available on medical databases.